The danger of moles: when you should see a doctor
Nevus (from Latin means “birthmark”) is a neoplasm familiar to absolutely every person. Moles are present on every person’s body and in most cases do not pose any health hazard.
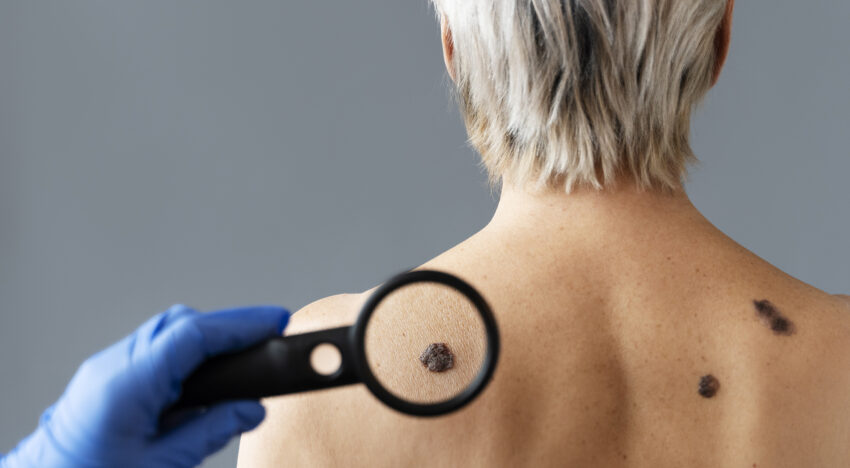
However, there are also situations when a benign formation on the skin becomes dangerous. Therefore, knowing what moles are, how to understand whether a mole is dangerous and how to treat them correctly is very important. This is exactly the kind of useful information we have collected in this article.
Why and where moles appear
Pigmented moles or melanocytic nevus are a very common benign formation on the skin, which appears as a result of local proliferation of pigment cells (melanocytes). It is due to the pigment that moles have a color that varies from light brown to almost black.
You can find moles on any part of the body – on the torso, limbs, scalp, face, feet and palms. Those with fair skin face more moles on their bodies than naturally dark-skinned people.
Moles can either be present on the body from birth (congenital nevi) or appear throughout life (acquired nevi). According to statistics, only 1% of people are born with one or more melanocytic nevi.
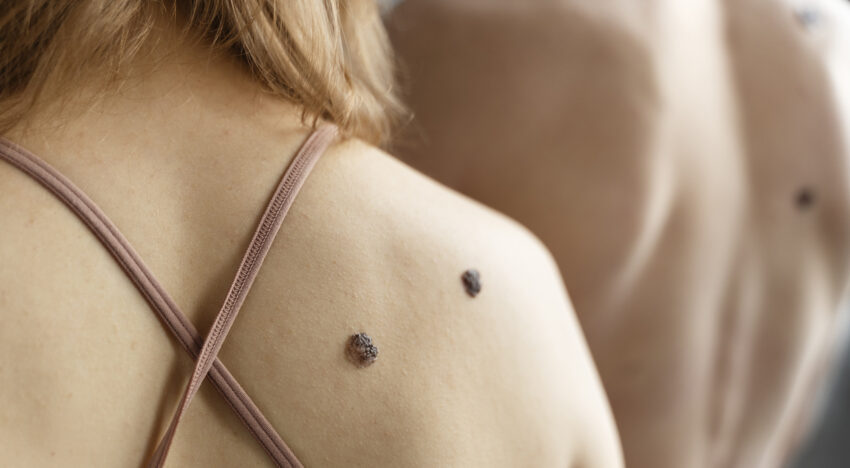
The appearance of moles is a process that occurs throughout life. It is also known that moles that appear between the ages of 2 and 10 years are the most noticeable and persistent. Moles that appear in adulthood are most often the result of exposure to the sun. Such moles may disappear or change over time.
Although there is no exact information about what causes moles, scientists still identify factors that contribute to their appearance. These factors include:
◼ genetic predisposition – people with many moles on their skin usually have relatives with similar skin;
◼ exposure to the sun – aggressive sun rays provoke many skin problems, including the appearance of new moles and mutations of existing ones;
◼ the state of the immune system – nevi may become noticeably more numerous when undergoing immunosuppressive therapy or using BRAF inhibitor drugs.
Types of moles
There are many types of moles, which differ in appearance according to three characteristics:
◼ shape – there are flat, hanging and convex moles;
◼ size – can be small (0.5-1.5 cm), medium (1.5-10 cm), large (10 cm or more) and giant (the whole area of the body);
◼ color – moles can be either skin color or have a grayish, cinnamon and black tint. There are also red and pink moles – angiomas.
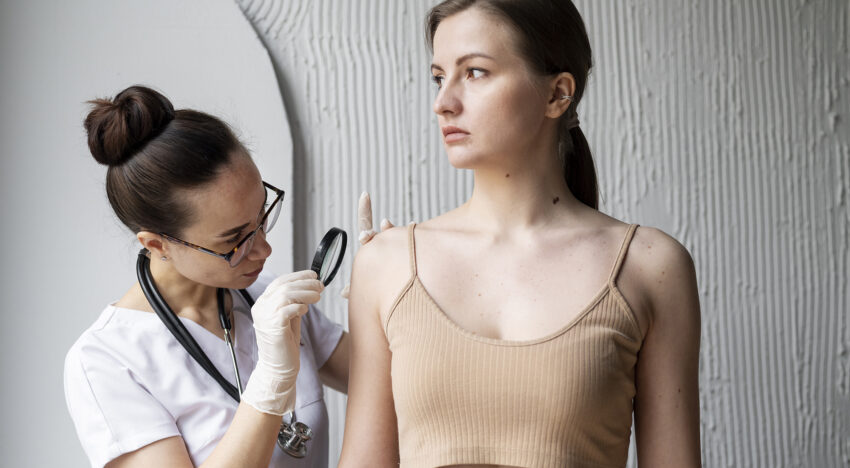
When conducting a detailed diagnosis, the doctor can determine a more precise name for the nevus:
◼ Intradermal – a birthmark with a large amount of pigment and clear contours.
◼ Halonevus – a formation with a large amount of pigment and a discolored rim.
◼ Giant (pigmented) – has a congenital character, medium or large size (often at least 5-7 cm).
◼ Involutional (fibrous nasal papule) – a raised, weakly pigmented formation near the wings of the nose, which appears as a result of fibrous degeneration of a mole.
◼ Borderline (functional) – most often a congenital phenomenon with an uneven brown color, which has a tendency to degenerate.
◼ Complex (mixed) – a small pigmented papule (often up to 1 cm).
◼ Blue – a nodule that has a characteristic blue undertone, most often appears as a single formation in adolescence.
◼ Epithelioid (spindle cell) – a small, light-colored nodule that most often appears on the face.
Only a certified dermatologist or oncologist can accurately determine the type of nevus and draw up a further plan of action after a thorough examination.
Methods for diagnosing and treating moles
In order to prevent benign moles from developing into dangerous ones, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the skin and all formations present on it.
How to recognize dangerous moles in time
Monitoring of moles and other formations is carried out using dermatoscopy. This is a procedure that involves carefully examining the skin using a special device – a dermatoscope. During a routine examination without a dermatoscope, it is often simply impossible to determine the signs of dangerous moles. The device allows the doctor to examine all formations at close range and determine whether processes hazardous to health are occurring on the skin.
This examination is absolutely painless. The procedure is performed by a dermatologist or oncologist.
Such preventive examinations by a dermatologist must be carried out every year. For people with the first skin phototype (fair skin with a lot of moles, blond/red hair, light gray or blue eyes) it is necessary to undergo an examination every 6 months. It is also worth making an appointment for an unscheduled inspection for everyone who observes
in all skin changes in the nature and size of nevi. Sun or any other burns are also a serious reason to visit a dermatologist and check whether the moles that are already on the body are dangerous.
With the help of regular examination of moles through a dermatoscope, the doctor will be able to track even the smallest changes and, if necessary, prescribe the appropriate treatment at a very early stage.
In more detail about when it is necessary to consult a dermatologist, we told in our video.
Differences between moles and melanomas
People worry about whether or not moles are safe on their bodies, as many have heard of melanoma, a malignant overgrowth of melanocytes that is the most common cause of death from skin cancer. At first, melanoma may look like a regular melanocytic nevus, but over time it becomes a disordered structure that tends to get larger.
The danger of moles can increase not only due to melanoma, but also due to aggressive sun exposure, during pregnancy or other circumstances.
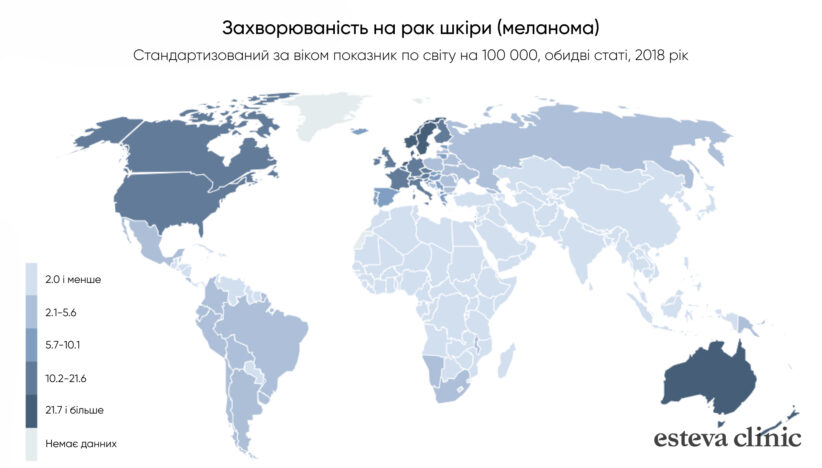
This frightening prospect often motivates people to diagnose and remove dangerous species. Those who have a large number of nevi on the skin (more than 100 pieces) should be especially attentive to formations.
There are several ways to help distinguish a mole from melanoma at home:
◼ the shape, size, structure or color of the nevus began to change;
◼ the formation has ABCDE characteristics (asymmetry, border, color, diameter, evolution);
◼ the nevus itches, bleeds or becomes crusty;
◼ by external signs the formation is different from all others on the body
◼ a new mole begins its development in adulthood, when a person is already 40 years old or more.
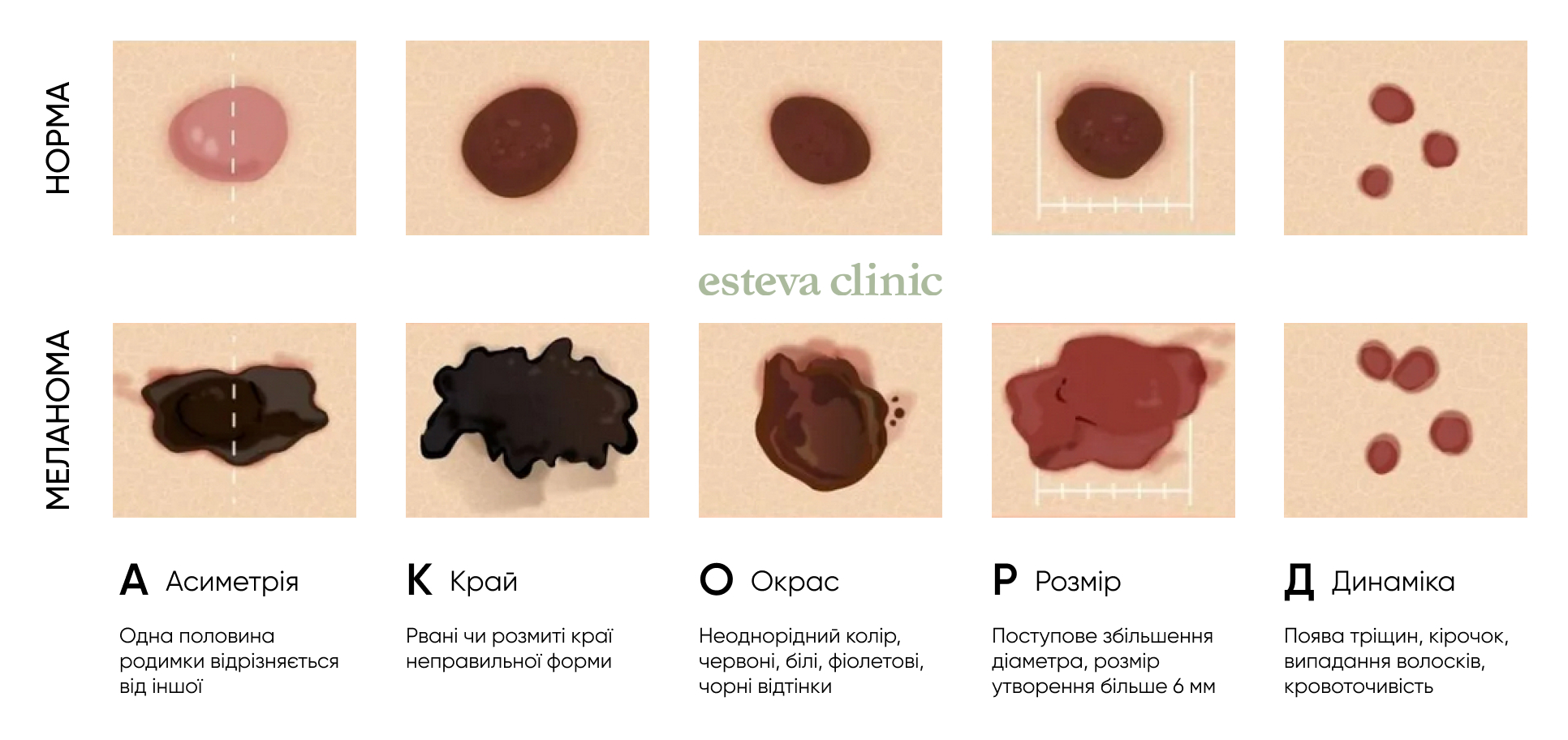
All these changes in the nevus are signs that the mole is dangerous to health. If you observe such changes, you should immediately consult a doctor, who can more accurately determine whether signs of atypical moles are present and draw up a further treatment plan.

Often people turn to a dermatologist specifically for the purpose of removing tumors on the skin that cause aesthetic discomfort. Only a doctor can determine whether it is dangerous to remove a mole after performing a dermatoscopy.
A mole must be removed if it:
◼ has signs of degeneration;
◼ is located in a place that is regularly susceptible to injury from clothing or something else;
◼ changes dramatically in size over a short period of time.
How are moles must be treated
The Esteva Clinic, an aesthetic medicine and cosmetology clinic, offers its clients several ways to remove unwanted or dangerous moles. They all have their own characteristics and are selected for each specific situation after an individual consultation.
◼ Radio wave method. Removal of skin tumors occurs using high frequency radio waves. The area with the nevus is first treated with an antiseptic, after which local anesthesia is performed. For this reason, removal of a mole is practically painless, and damage to the skin adjacent to the nevus is minimal.
◼ Laser removal. A modern and safe way to get rid of benign tumors. Removal occurs using a laser beam, which burns out the nevus with minimal trauma to the skin around it.
◼ Cryodestruction. A procedure during which is used deep freezing of tissues. As a result, the process of cryonecrosis – dying occurs. The wounds heal under dry crusts that peel off after 2-3 weeks. The disadvantage of the procedure is that it is difficult for the doctor to control the depth of cold exposure, and therefore minor burns or scarring of the skin may occur as a result.
You can also learn about how tumors are removed at Esteva Clinic in our short video.
In addition to removing existing lesions, your doctor will help you choose a daily care routine that is ideal for your skin type. This approach will help stop the appearance of new moles in the future, because nevi often appear precisely due to the lack of proper sun protection (SPF creams, closed clothing) or improper care of the face and body.
Видалення родимок та невусів
| Назва процедури | Ціна, грн |
|---|---|
| Консультація дерматолога обов’язкова | 790 |
| Контроль після видалення з 30 по 45 день | Безкоштовно |
| Родимки, травмовані новоутворення, невус, поліпи - видалення з гістологією новоутворення до 1 см | 2300 |
| Родимки, травмовані новоутворення, невус, поліпи - видалення з гістологією новоутворення до 2 см або на повіці | 3300 |
| Родимки, травмовані новоутворення, невус, поліпи - видалення з гістологією новоутворень до 1 см до 3 шт | 5900 |