Eczema and dermatitis – what’s the difference

The frequency of visits to a dermatologist for eczema or dermatitis, according to statistics, is 15-20%, and 20-40% of all dermatological ailments may be hospitalised with this diagnosis. It is the most common skin disease, affecting men and women in equal proportions, predominantly of active age.
Such a large number of sufferers makes it necessary to address the topic again and again:
- to find out if there is a difference between eczema and dermatitis;
- what causes the skin lesions;
- whether there are effective drugs or treatments for dermatitis and eczema;
- how to prevent dermatitis.
The specialists at the Esteva Clinic of Aesthetic Medicine and Dermatology share their knowledge on these issues, and are invited to individual consultations to find the right treatment for dermatitis and eczema for the individual patient, and to develop preventive measures to achieve a sustained remission.
Is there a difference between eczema and dermatitis
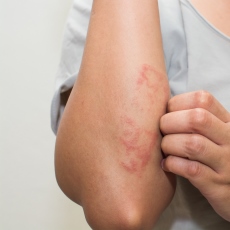
Eczema is a skin condition with a red, itchy, moist rash in the acute phase, resulting in dry and thickened skin, peeling and sometimes darkening of the skin. The incessant itching and scratching that it causes not only disfigures your appearance, but also prevents you from sleeping and working properly and can provoke neurological reactions, including insomnia.
The question of the difference between dermatitis and eczema makes no medical sense, as they are different names for the same disease.
In the literature, these terms are used as synonyms, and we will also adhere to this tradition, although medically it is still more correct to speak of eczema.
The disease has an acute and chronic form, is not transmissible from person to person, and the sufferer can go a long time without any manifestations of the disease. Achieving a long-lasting remission is the main objective in the treatment of dermatitis and eczema.
External manifestations of dermatitis
In the acute phase, eczema and dermatitis manifest as redness (erythema) without clearly delineated borders, with the simultaneous appearance of microbubbles that burst when scratched, immediately forming deep, pitting erosions. Fluid is excreted from the erosions, followed by the formation of a crust. All these processes occur in a wavelike pattern and appear to occur simultaneously.
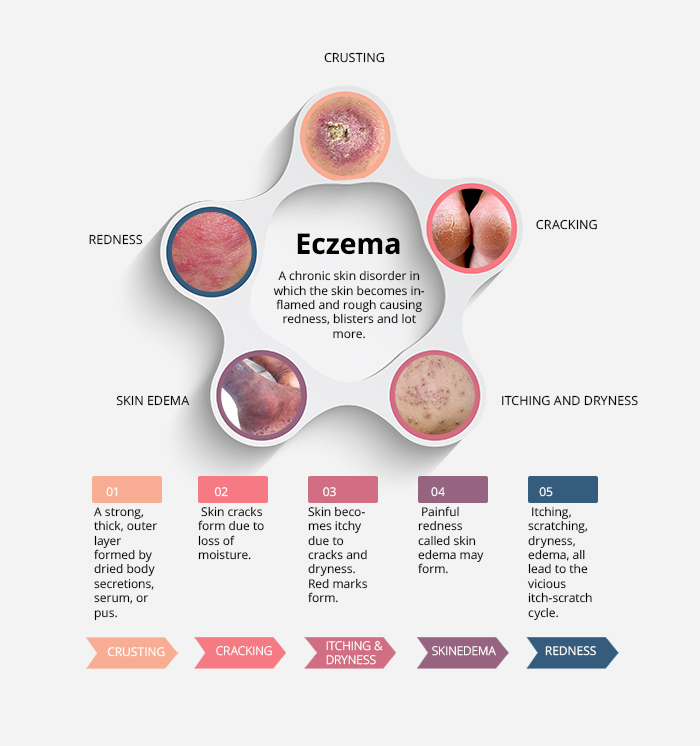
In the acute stage, there is severe itching that is difficult to relieve. This is a characteristic feature of the disease.
When the acute process has subsided, the skin thickens, and streaks and patches of healed wounds may remain. Sometimes there is lichenification, which is a persistent, distinctive skin pattern on the site of the former acute process.
⚠️ Deep wounds and scars can form on the skin in advanced cases or with improper treatment
Whatever the cause of dermatitis, treatments and medication should be prescribed by a qualified professional.
Types of dermatological disease
Eczema and dermatitis differ both in the severity of the process, as described in the previous section, and in the causes, which we discuss below.
Eczema and dermatitis depend to some extent on heredity. It is claimed that 40% of those affected have a history of some form of allergy in one of their parents. If both parents suffer from asthma, allergic rhinitis or other conditions of an allergic nature, the risk of the disease occurring in their children is increased by up to 60 %.
Diseases of the internal organs, in particular the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system, and external stimuli such as chemical burns, mechanical damage and bacterial contamination may also provoke the disease.
Note that all types of dermatitis may recur to varying degrees at different intervals. The only way to avoid recurrence, or at least make it as rare as possible, is through a proper diet, a healthy lifestyle and strict adherence to medical advice. Preventive measures will be discussed later.
Types of dermatitis
As mentioned above, there is no distinction between eczema and dermatitis, so let’s look below at the types of disease depending on the causes and contributing factors.
We remind you that all information is of an informative nature and should not be used as a basis for self-treatment.
It is now generally accepted that eczema is a multifactorial disease of an allergic nature.
The following types of eczema are distinguished according to their clinical manifestations and causes:
✅ true, or idiopathic;
✅ microbial (infectious, mycotic, nuchal translucent, varicose);
✅ seborrheic;
✅ professional;
✅ children’s.
Alternative names include atopic eczema, skin allergy, herpes simplex, venous, allergic or dyshidrotic eczema. These are essentially names for variations of the same condition.
❗️ You can get a professional consultation with a dermatologist at our clinic by visiting a doctor at a convenient time. This is the only right way to get a proper diagnosis and adequate treatment ❗️
Виды экземы

📌 In simple eczema, the skin lesions are usually symmetrical, predominantly appearing on the face and hands, without clearly defined boundaries. This is the difference between eczema and dermatitis caused by an allergic reaction to some contact irritant, where the skin turns red at the site of the allergen. If you don’t know what caused this reaction, a series of allergy tests should be performed.
📌 The microbial form is caused by a bacterial or fungal infection of the damaged skin. It happens as a result of trauma suffered when an infection enters the unhealed wound.
📌 The varicose form can occur as a consequence of the development of varicose veins; at the site of ulcers, fistulas, or wounds.
📌 The common shingles can also be one of the causes of eczema
📌 Very unpleasant is pomfolix – dyshidrotic eczema: tiny itchy blisters (or blisters) that form under the skin on the palms of the hands and feet. As the skin here is thicker, there may not be any redness and the blisters may look like a millet grain.
📌 The seborrhoeic variety affects the scalp, can be on the auricles and behind the ears, sometimes in the chest area.
When is it worth seeing a doctor?
The disease can occur at any age.
If you notice symptoms:
✔️ a rash on the skin accompanied by severe itching;
✔️ redness;
✔️ bursting blisters and soaking sores;
⚠️ Do not delay visiting a doctor. You need a professional examination to get a proper diagnosis.
It has been described above how varied the forms of the disease can be. At the same time, you should distinguish between eczema and neurodermatitis and differentiate it from other dermatological conditions. This is difficult for a non-specialist to do, so an appointment with a dermatologist should be made.
Trying to find out on the internet how to treat atopic dermatitis, may end badly. The uncontrolled use of medication can lead to non-healing trophic wounds, huge scars and a thick, dark crust. Such effects are extremely difficult and sometimes impossible to treat.
The treatment prescribed by the doctor will necessarily include dietary food, possibly light therapy (phototherapy), external creams and oral medication.
Injections, intravenous infusions and hormonal medicines may also be used. Methods and techniques are selected according to the severity of the condition and the etiology of the disease.
People often ask us: Is eczema transmitted or not by shaking hands, working in a common room or having intimate contact? The answer is that the disease is allergic in nature, it is not infectious and is not transmissible from person to person. A soggy, red skin is unpleasant and distressing to the person affected, but not dangerous to outsiders.
Preventing dermatitis or eczema
Unfortunately, eczema cannot be cured permanently, but it is possible to achieve a significant improvement and a long-lasting remission, when a person does not think of his or her condition for years. There are a few essential rules for this:
✅ During active treatment, adhere strictly to your doctor’s instructions;
✅ do not self-medicate;
✅ exclude from your diet foods that may cause allergies (citrus fruits, nuts, fish and fish products, coffee, chocolate, smoked foods, vinegar, mustard, mayonnaise and other spices, horseradish, radish, tomatoes, aubergine, mushrooms, eggs, milk, strawberries, melon, pineapple, honey);
✅ alcoholic drinks and cigarettes are strictly forbidden;
✅ wear cotton clothing, wool and some synthetics are best avoided;
✅ do not stay in direct sunlight;
✅ avoid dusty and hot rooms;
✅ avoid contact with aggressive household chemicals, use neutral hypoallergenic products for washing;
✅ avoid stress.
✅ Scratches on the skin can be an open gateway for infections; avoid getting hurt.
Too hot water, soap or its analogues serve as irritants, avoid them.
Prevention of eczema includes careful selection of cosmetic products that may contain medicinal ingredients.
If triggers for a flare-up are identified, their effects should be eliminated. For example, if eczema is caused by handling chemicals (which can occur not only in industrial plants, but even in normal hair dyeing processes), the irritant should be eliminated immediately and no further use should be made of it, or you should work in a safe way – wearing gloves and other personal protective equipment. If this is not enough, consider changing your activity.
In remission, it may be useful to take a spa treatment for general recovery, immunity support and rehabilitation.
Conclusions
⚠️ Self-medication is dangerous!
A comprehensive examination can identify the exact etiology of the disease and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Our dermatologists, who have extensive experience, will choose an individual course of treatment and, if necessary, refer you to specialists in related fields: allergologist, gastroenterologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, vascular surgeon.
Before and after photos of our patients (watch us on Instagram 🙂) you can learn more about the results of the work of our clinic doctors.
Lifestyle, diet and clothing play an important role in the maintenance of normal functioning. The battle against eczema is always a teamwork of doctor and patient, where the outcome depends on the perseverance of the latter perhaps more than the medication.
Come for a consultation, and be well!
Консультация дерматолога
| Наименование консультации | Цена, грн |
|---|---|
| Консультация специалиста | 590 |
| Повторная консультация (до 14 дней после первичной консультации до 20 минут) | 390 |
| Консультация специалиста в день проведения косметологических/дерматологических процедур (до 20 минут) | Бесплатно |